
After numerous scandals like the Equifax data breach and the 2016 US election, cybersecurity has become a significant issue for Americans. Unfortunately, anytime we use our devices, we're open to a cyber attack — especially when we browse the web. However, there are ways that we can make it harder for hackers and data miners.
The biggest security weakness in your smartphone is its data connection — sadly, any device with always-on internet access will inherently carry risk. Although there are no foolproof methods, by using the following suggestions, you can better protect yourself from Russian hackers, big data, or even a nosey spouse.
- Don't Miss: The Best Phones for Privacy & Security
Step 1: Get a VPN
Perhaps the single best way to improve your defenses while browsing the web is to use a VPN. A VPN (or Virtual Private Network) can offer two major security features: encryption and privacy.
With the right VPN, all your data is encrypted during transit. Think of it this way: instead of driving your data in a regular car, it is now traveling in an armored truck. It may move slower, but it will be a lot harder for someone to access it while it is traveling from your phone to whatever website you're visiting.
The second feature that a VPN provides is privacy. Your IP address is equivalent to your mailing address at home. Similar to how the post office uses your mailing address to send letters, your IP address is used by your network to move data between your device and the internet. Without a VPN, it is easy for someone to obtain the IP address of your device for a direct attack against your smartphone.
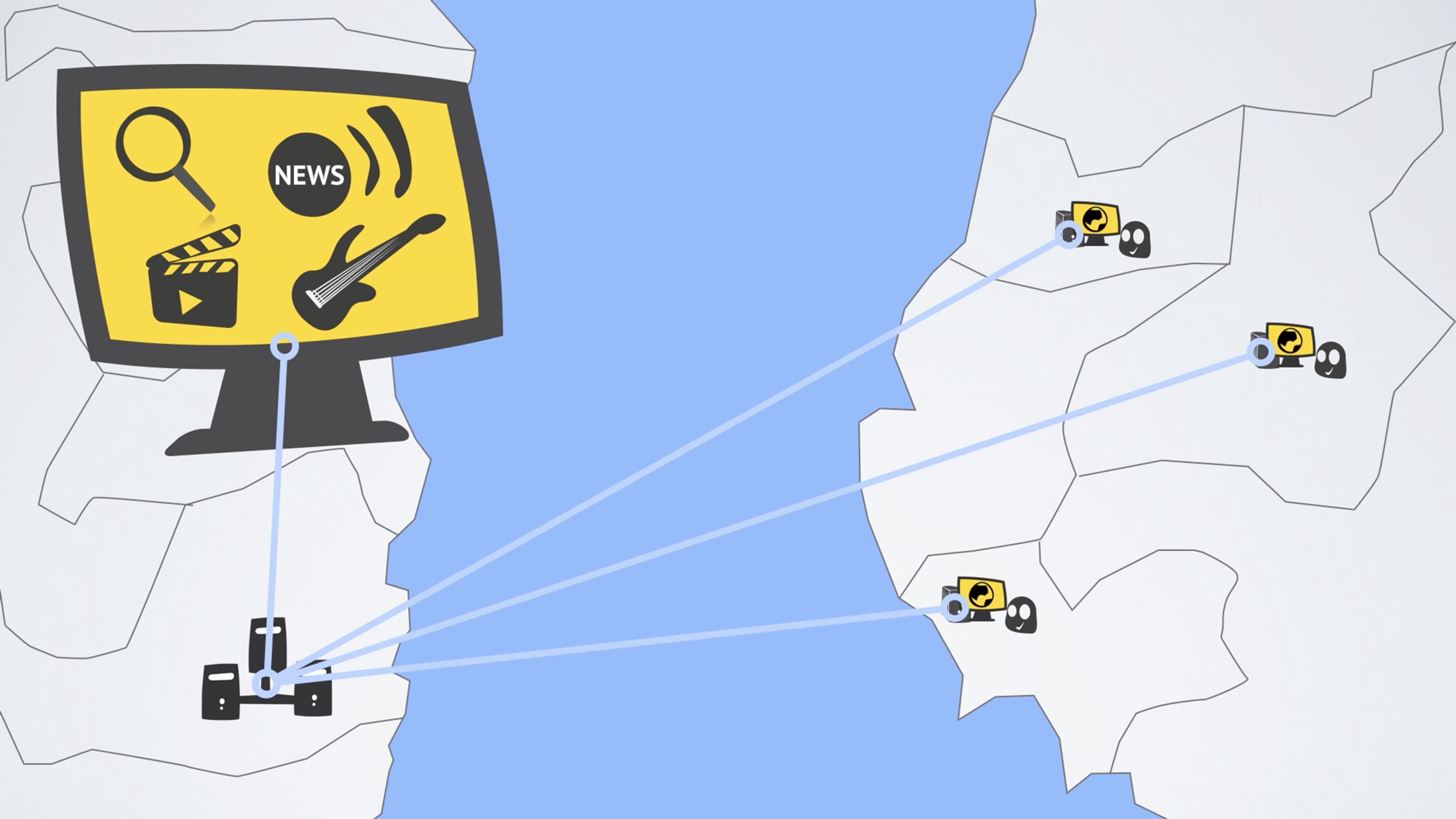
VPNs create a secure tunnel between your Android device and the server (or router) that provides the VPN service. This server acts as a buffer between you and the internet. Imagine every time you send a letter, you give it to the mailman, who places the letter into another envelope marking the sender as himself. Now if someone comes across the letter, they would believe that it originated from the mailman and not you.
VPNs work the same way. Whenever you send data to the internet, it will go through a secure server first before heading out to the web, which marks the traffic as if it originated from the VPN server. Now if a packet is intercepted by a malicious entity, they won't have your IP address, but the VPN's instead.
With the 2017 ruling by FCC to effectively end Net Neutrality, privacy is more important than ever. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) once again have control over all data that runs through their networks and can do whatever they see fit.
As history has shown, ISPs will regulate traffic based on the kind of websites you visit or the services you use. With a VPN, your ISP doesn't see what sites you visit — all it sees is an encrypted connection between you and your VPN. Therefore, your ISP can't downgrade your Netflix movie quality or block your device from a specific service. It also can't effectively record your browsing history to sell to corporations. Unless your ISP blocks VPN traffic (which is possible), using a VPN is one of the only ways to surf the web privately and freely.
There are many excellent VPN services on the Play Store, but my personal favorite is NordVPN, as it provides a great balance of security and speed. NordVPN uses the highest encryption method to protect your data and has over 2,400 servers in 56 countries, allowing it to maintain fast speeds while doing so.
- Play Store Link: NordVPN (free)
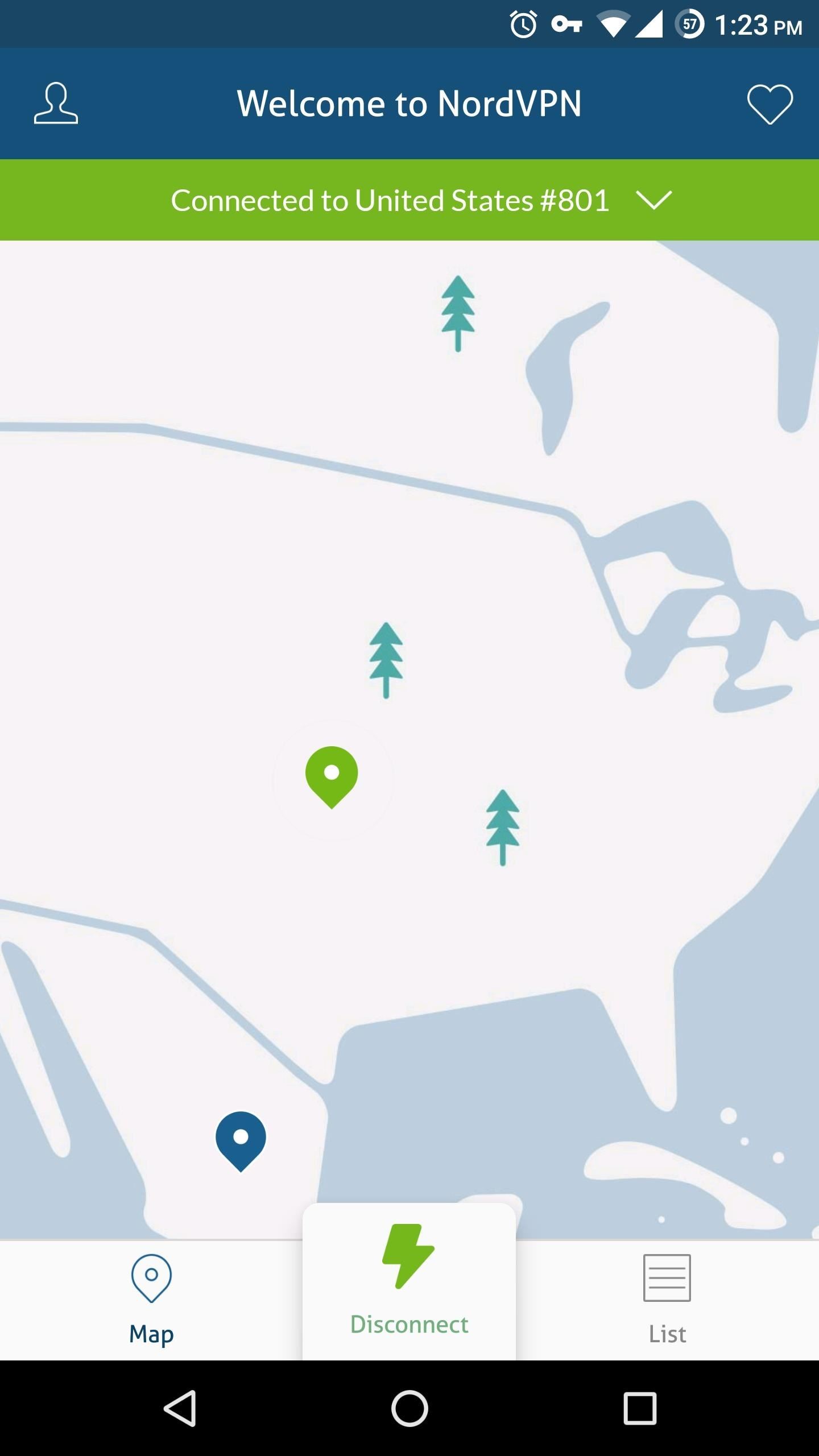
Its Android app is very simple and straightforward. Once you open the app, create an account, and log in, just select "Quick connect" from the main page. After confirming your choice on a system dialog, NordVPN will connect you to the nearest server with the lowest traffic, ensuring minimal loss of internet speed while using VPN protection.
NordVPN also has a feature known as CyberSec, which provides additional protection by actively monitoring the websites you visit to protect against malware, ads, and botnet (attacks which use your smartphone to attack other devices).
- Don't Miss: The Best VPN Apps for Android & iPhone
Step 2: Start Using a Password Manager
With so many different accounts, it's hard to come up with a unique and creative password for each one. Unfortunately, weak passwords are one of the leading ways hackers access personal information. Whether your password is found through a brute-force attack or something like one of Yahoo's data breaches, if you used the password on other sites, those accounts are now compromised, too.
So the best practice is to use a different password for every account, and to make sure those passwords are all random alphanumeric combinations that use special characters. However, obscure passwords like these are hard to memorize once, let alone for every internet account you have. Password managers solve this problem.

With a password manager, you only need to memorize one password to access a database of all your other passwords. Whenever you create a new account, you use the password manager to generate a password, selecting from a range of criteria to both fit the requirements of the site and make the most secure password possible. Now, whenever you enter that website or app, you can fill in your password by copying it from the database.
LastPass is one of the best password managers found on the Play Store. It is one of the only password managers that allows you to autofill your information. Not only is autofill convenient, but it also provides security from hackers. If a hacker gains access to your device, they may employ key logging, which records each key you press on your screen — but with autofill, there are no keys to log.
- Play Store Link: LastPass Password Manager (free)

LastPass also stores the password database on your device, preventing the possibility of someone intercepting it if it was stored remotely. It also employs the highest encryption protocols to protect your database, and allows the use of both two-factor authentication (using both a password and temporary PIN code via text or e-mail) and fingerprint authentication to protect your database better.
- Don't Miss: The Best Password Managers for Android

Step 3: Install a Secure Browser
Chrome is an excellent browser for its ease of use and fast performance, but if you want to protect yourself from external threats, we recommend switching your default browser. Using a secure browser is important, because by default, most browsers try to balance security and speed with a heavy emphasis on speed. Browsers also accommodate corporations who wish to sell you advertisements. However, these accommodations can be used to harm you as well.
Cookies are small text files sent by web servers to help identify you and personalize your experience on a web page. For example, the way Amazon and eBay can recommend products is by use of cookies. However, these cookies can be altered to allow unauthorized access to your smartphone.
Websites employ trackers which monitor sites every time you view a page. These trackers report information to a server so companies have a better understanding of their customers. They are used to enhance the experience and personalize your view (cookies are sometimes used as a tracker). However, they also can be used for malicious purposes.
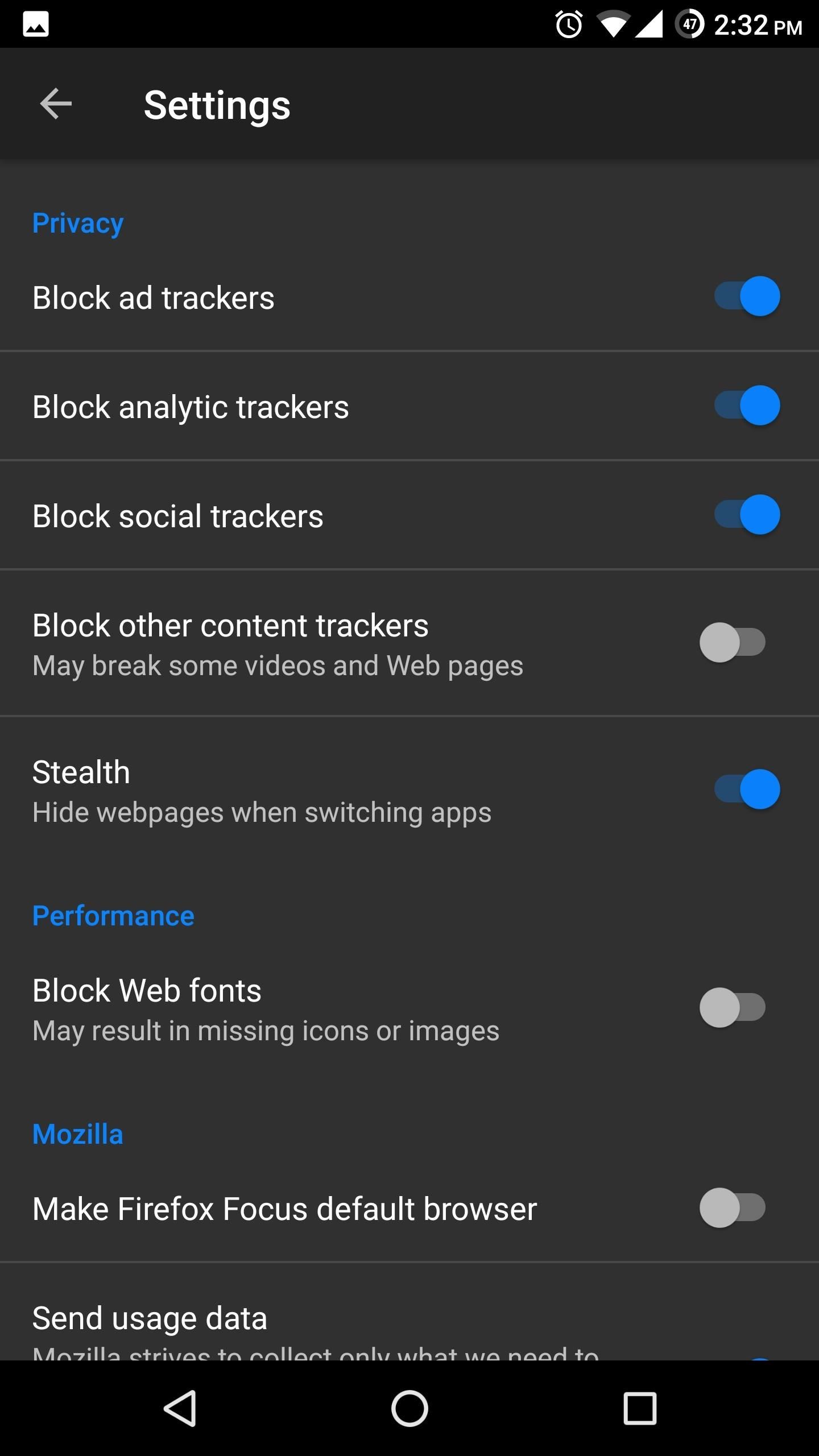
Although you can manually disable cookies and trackers in Chrome, there's a browser that does this by default. For that reason, we recommend Firefox Focus.
- Play Store Link: Firefox Focus (free)
With Firefox Focus, Mozilla has created a browser that focuses on security and speed, but emphasizes security. Almost all trackers are blocked by default, with only ones that can disrupt the viewing of the web page allowed. Sites are also prevented from opening a malicious website in another tab without you knowing.
With all this blocking, it is one of the fastest browsers on the Play Store, since when it loads pages, it doesn't have to load ads (which typically take some time). And whenever you close Firefox Focus, it deletes all cookies and your browsing history. So if you decide to look at more, um, Christmas gift ideas, you don't have to worry about someone seeing your activities.
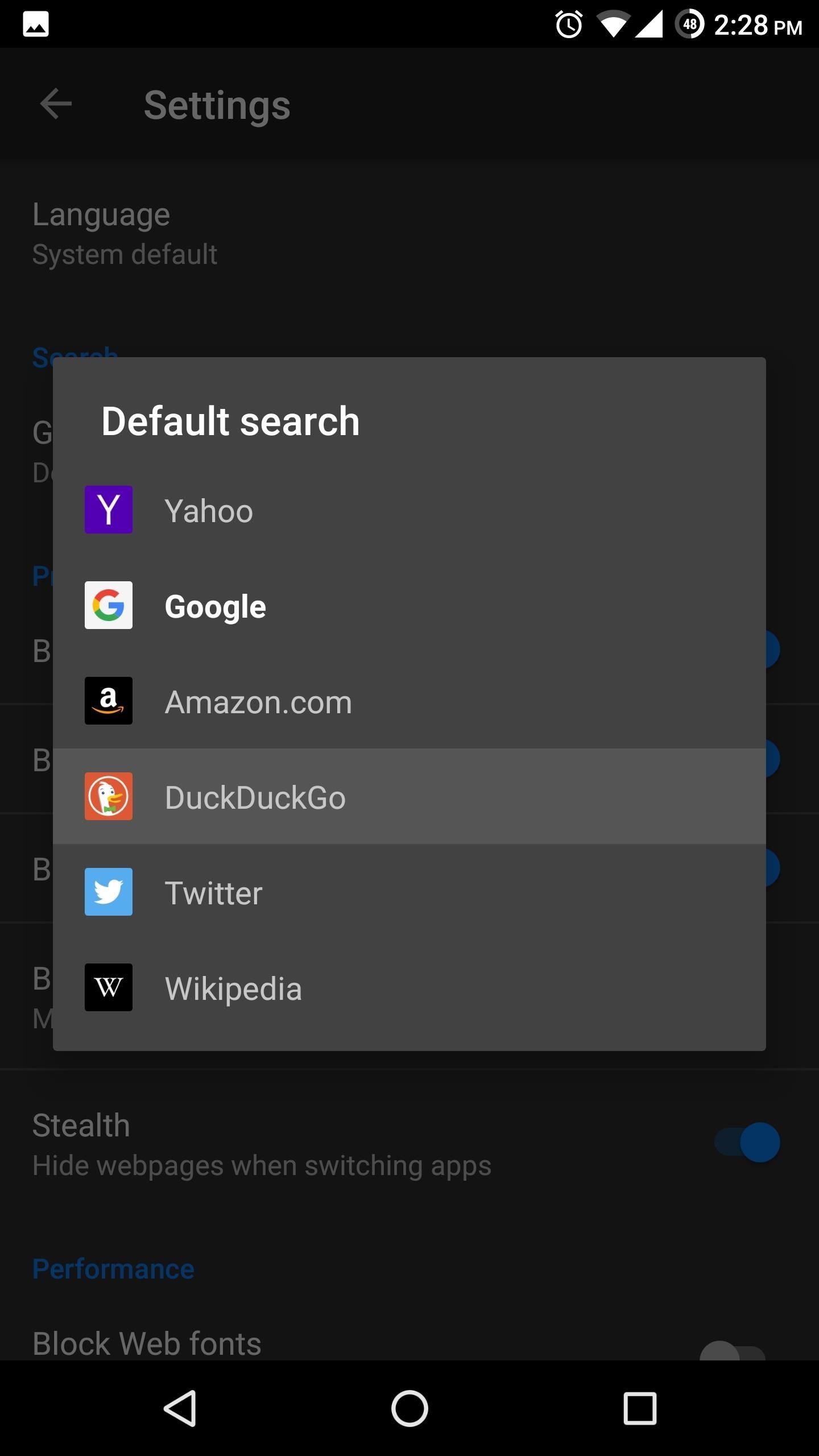
When using Firefox Focus, we also recommend switching the default search engine. With Firefox Focus open, tap the three vertical dots in the upper-right corner and choose "Settings." From there, scroll down to the Search section and select the first option, then switch it to DuckDuckGo. DuckDuckGo is the only search engine on the list that doesn't collect your search result information.
Step 4: Take Care of the Little Things
Beyond the apps we just discussed, we have a few more recommendations to improve internet security. The first is to use HTTPS as often as possible. Most popular websites all will redirect you to the HTTPS version of their website, but if you happen upon a site without it, don't enter Personally Identifiable Information.
HTTPS provides encrypted communication between your smartphone and the website's server. Although the encryption isn't the highest level to ensure speed isn't significantly reduced, it does provide some protection where HTTP offers none. A VPN addresses this by providing encryption that does employ the best standards currently available. However, using HTTPS is still good practice.

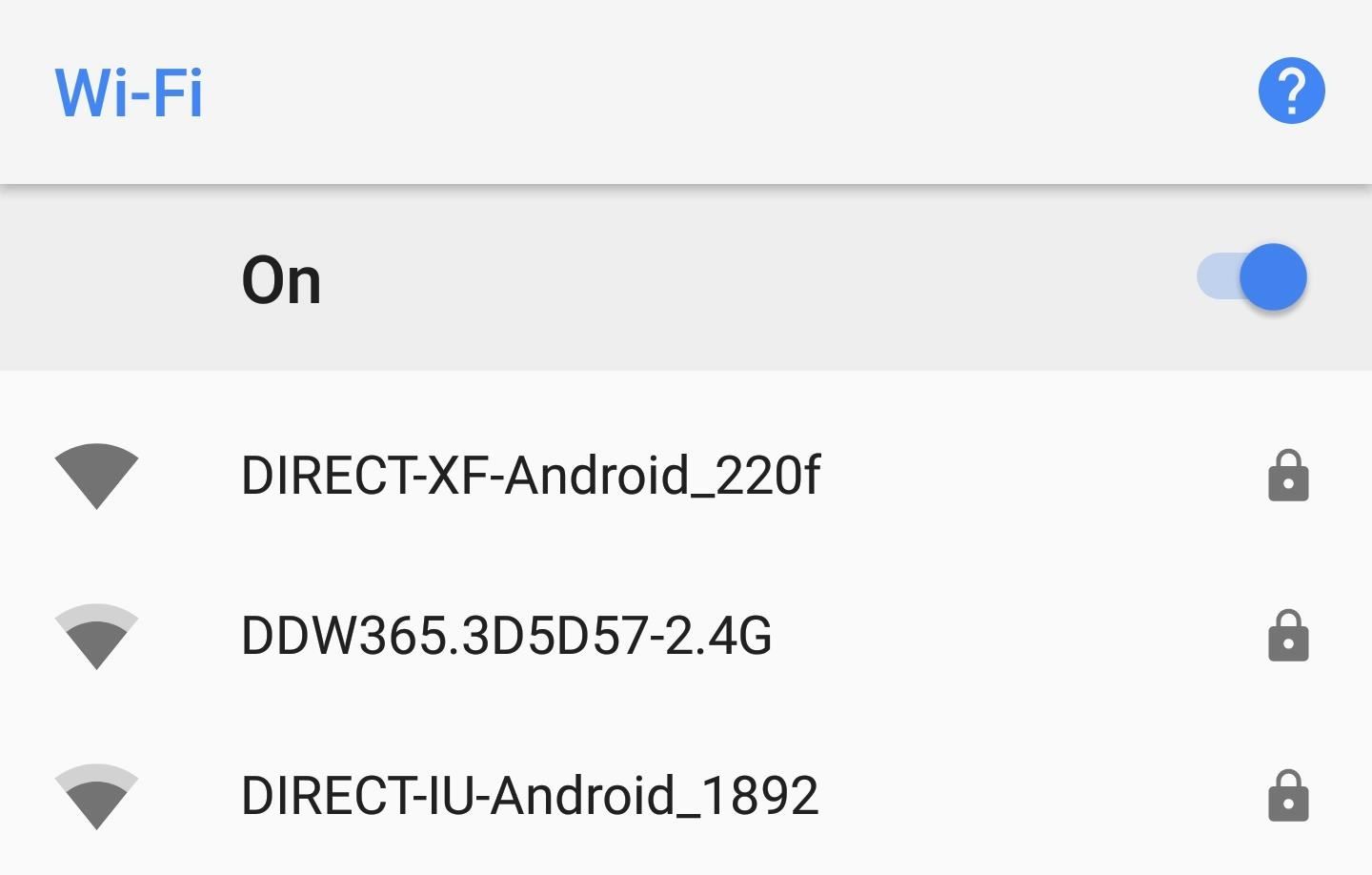
Our second recommendation is to avoid using public Wi-Fi, as these are unsecured networks that are susceptible to cyber attacks. It can easily be used by a malicious agent to learn your IP address and attack your device.
Public, unsecured networks can also be spoofed, which is when a hacker will create a fake Wi-Fi hotspot that shares the same SSID as the public Wi-Fi. Therefore, when you connect to the network, you believe you are using the public Wi-Fi, but actually are connected to a hacker's machine sending all your data to them. Like the first recommendation, VPN provides protection, but it's a good practice to follow.
Finally, always be careful about the sites you visit. Try to stick to popular websites instead of obscure ones. Avoid links to websites from individuals you don't know, and make sure you type website names correctly. A known tactic by hackers (called "phishing") is registering a website name for common spelling errors associated with a popular website (e.g., "goggle.com").
If you stumble on a phishing attempt, instead of going to the site you want, you're directed to the hacker's site, which can be designed to look exactly like the popular one. You think you're on the popular website, so when you log in, you're sending your user name and password to the hacker.
These recommendations will not completely prevent you from a cyber attack, but they'll certainly go a long way. In the end, the goal is to safely browse the web while keeping your information and history private. So whether you are scared of hackers or you don't want your significant other to see your browsing history, these recommendations should provide a great start.
This article was produced during Gadget Hacks' special coverage on smartphone privacy and security. Check out the whole Privacy and Security series.
Who needs a wand? Unlock your magical powers and transform yourself from a Muggle into a Wizard or Witch just by using your Android phone. See how:












Be the First to Comment
Share Your Thoughts